
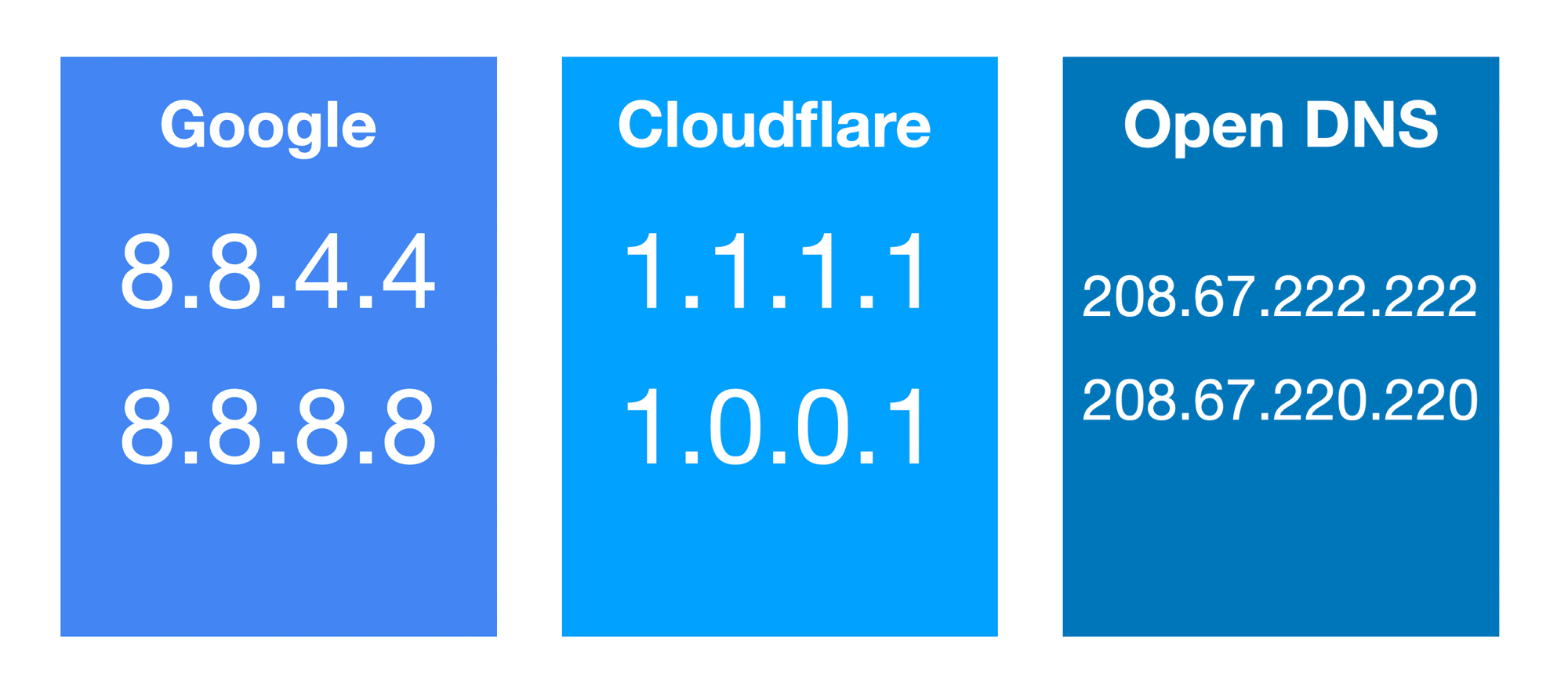
Using a more straightforward, more memorable name in place of the numeric address of a host goes back to the ARPANET age. Users benefit from this when they use significant Uniform Resource Locators (URLs), without needing to understand how the services are really located by the computer and e-mail addresses. Unlike a phone book, the DNS could be instantly upgraded, enabling the place on the network to alter without changing the end users, who continue to make use of the exact same host name of a service. For general purpose uses or whether for Internet naming, the DNS database is kept in a zone file that was ordered.Īn often-used analogy to spell out the Domain Name System is the fact that it functions as the telephone book by interpreting individual-friendly computer hostnames.

DNS has additionally seen use in fighting unsolicited e-mail (junk) by employing a realtime blackhole list saved in a DNS database. To get an entire listing of DNS record types, start to see the set of DNS record types. Although not meant to be a general purpose database, DNS can save records for other kinds of data for either automatic machine lookups for things or for human queries like responsible individual (RP) records. The most frequent forms of records saved in the DNS database are those coping with a DNS zone’s ability power (SOA), IP addresses (A and AAAA), SMTP mail exchangers (MX), name servers (NS), pointers for reverse DNS lookups (PTR), and domain name aliases (CNAME). A DNS name server is a server that stores the DNS records to get a website name a DNS name server reacts with responses to queries against its database. Internet name servers and a communication protocol execute the Domain Name System. The Domain Name System keeps the domain name hierarchy and offers translation services between it as well as the address spaces. The web keeps two principal namespaces, the domain name hierarchy as well as the Internet Protocol (IP) address spaces. Historically, other directory services preceding DNS are not scalable to big or global directories as they were initially according to text files, conspicuously the HOSTS.TXT resolver. It defines the DNS protocol, a comprehensive specification of data communication exchanges and the data structures used in DNS, within the Internet Protocol Suite. The Domain Name System additionally defines the technical functionality which will be at its heart. This mechanism supplies distributed and fault tolerant service and was made to prevent the dependence on a principal database that is single. Authorized name servers are delegated to lead to their domain names that were supported, and could delegate power over sub domains to other name servers. The Domain Name System spreads the duty of assigning domain names by designating authorized name servers for every domain name and mapping those names. The Domain Name System is a critical part of most Internet services’ functionality as it’s the primary directory service of the Internet.

Most conspicuously, it interprets domain names, which people can easily memorize, to the numeric IP addresses required for the goal of apparatus and computer services world-wide. It links domain names assigned to all the participating things and various advice. The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical distributed naming system for some resource, services, or computers on a private network or the web.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
